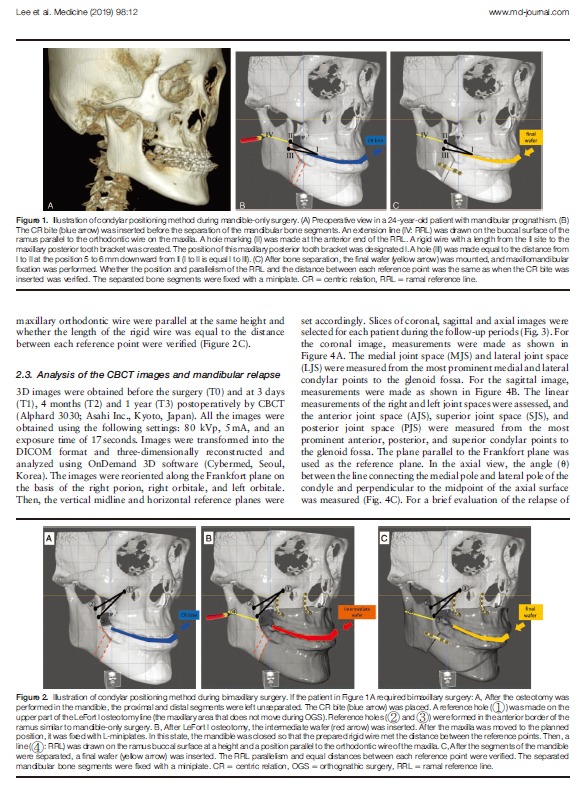
Three-dimensional assessment of condylar position following orthognathic surgery using the centric relation bite and the ramal reference line(A retrospective clinical study)
English 2022-08-25 PDF Lecture 395
Author
마케팅
Date
August 25, 2022
Abstract
Orthognathic surgery (OGS) is a relatively common procedure for solving functional and aesthetic problems in facial and jaw areas in
patients with dentofacial deformities. The positioning of the mandibular condylar segment during OGS has an impact on the surgical
outcome. This study aimed to investigate the changes in the condyle-fossa relationship three dimensionally after OGS using the
centric relation (CR) bite and the ramal reference line (RRL).
Thirty-two patients with skeletal malocclusion underwent OGS. Condylar repositioning was performed using the CR bite, as
previously reported. A RRL was added to the existing method and used during the surgery. Cone-beam computed tomography
scans were acquired at 4 time points. Sixty-four condyles were evaluated in the coronal, sagittal, and axial views. Two groups were
created according to the amount of mandible setback (SB1 vs SB2), and another 2 groups were created according to the maxillary
operation (1-jaw vs 2-jaw). Each was then compared at the 4 time points. Differences between the values before (T0) and a year after
surgery (T3) were also investigated. The positions of the pogonion and the menton were examined at T2 and T3 for the simple
evaluation of relapse.
The change in the condylar position was significant over a time-course (P<.001) but not between T0 and T3 (P>.05). Neither the
setback amount nor the maxillary operation affected the positional change (P>.05). There were no significant changes between T2
and T3 in the relapse evaluation.
This condylar repositioning method using the CR bite and a RRL showed stable results after OGS. This method is noninvasive and
cost-effective and can be easily performed even by an inexperienced surgeon because it reduces errors in repositioning the condyle
during OGS.
Abbreviations: 2D = two-dimensional, 3D = three-dimensional, AJS = anterior joint space, CBCT = cone-beam computed
tomography, CR = centric relation, IVRO = intraoral vertical ramus osteotomy, LJS = lateral joint space, MJS = medial joint space,
OGS = orthognathic surgery, PJS = posterior joint space, RRL = ramal reference line, SJS = superior joint space, SSO = sagittal split
ramus osteotomy, TMD = temporomandibular disorder, TMJ = temporomandibular joint.
Keywords: cone-beam computed tomography, craniofacial, orthognathic