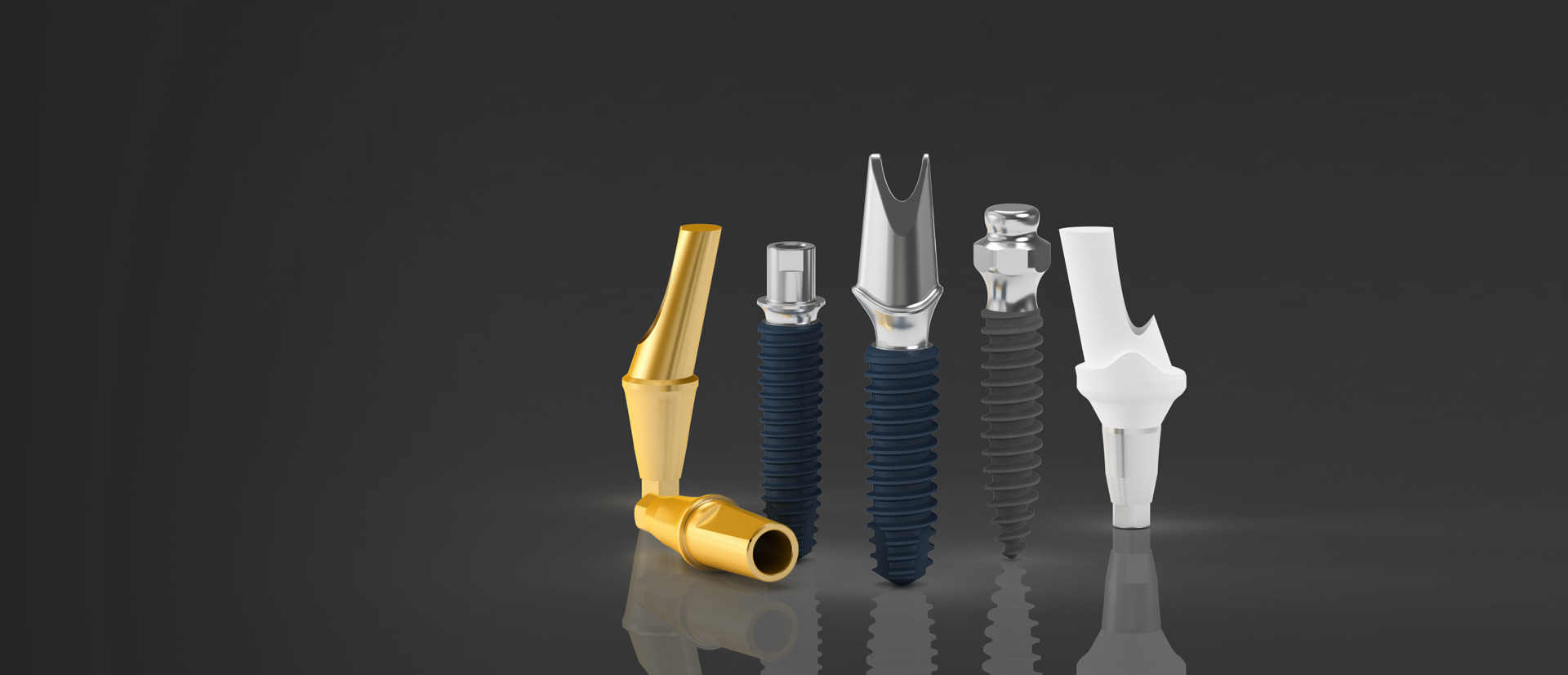
Key Advantages
- Excellent 2-piece solution for maxillary lateral incisors & mandible anterior
- Easy-to-use, intuitive surgical procedure
- Excellent esthetics
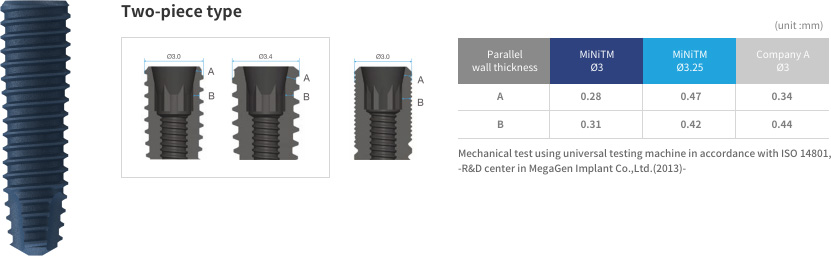
MiNi™, but mighty
In comparative tests, MiNi™ Ø3.0 showed similar compressive strength, while MiNi™ Ø3.25 showed much higher wall strength
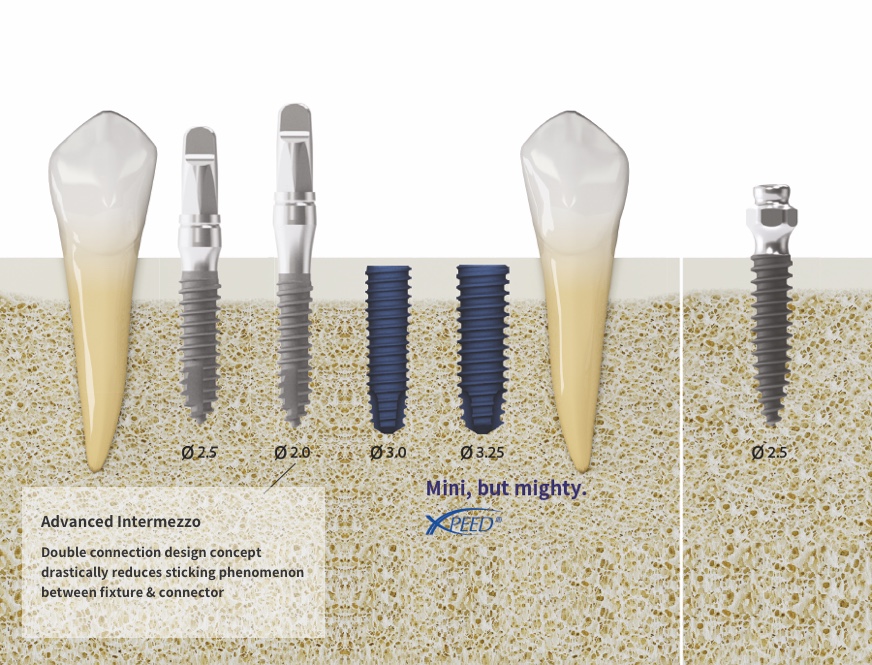
Fixture Lineup

Overdenture type
Minimizes drilling sequence with 1-step insertion
Abutment & Prosthetic Options
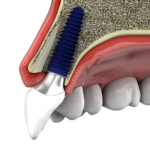
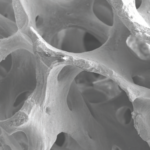
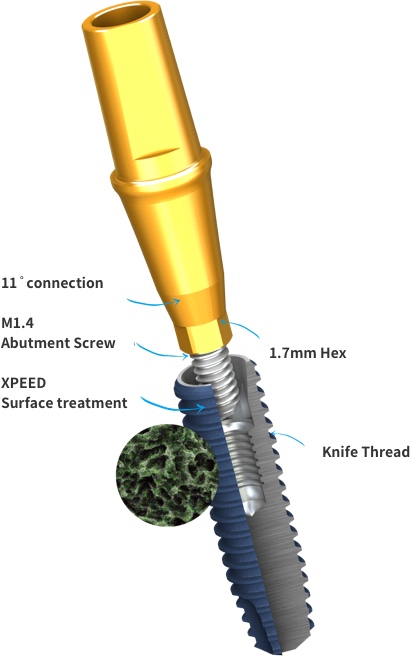
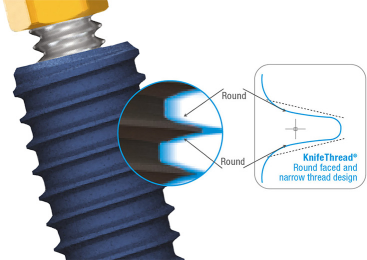
KnifeThread ®
Special thread design & super self-tapping create better initial stability in any compromised bone situation.
This distinctive design enables bone condensing, gentle ridge expansion, maximized compressive force resistance, & minimized shear force production.¹

- Strong
- Faster
- Safer
To promote secondary stability, all MiNi fixtures have a special extra surface coating called Xpeed. This unique hydro-thermal incorporation of calcium ions has already been proven to activate osteoblasts and accelerate osseointegration, essential for secondary stability.4,5 Plus, Xpeed provides an important quality check to avoid any acid residue (BLUE means NO acid residue!)2,3
Tips!
- Do not use torque wrench
- Max uniform strength of hex is 50Ncm
- Do not exceed 75Ncm
References
- McCullough JJ , Klokkevold PR The effect of implant thread design on implant stability in the early post-operative period
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27699890 - S.-Y. Lee, The cytocompatability and osseointegration of Ti implants with Xpeed surfaces
http://www.megagenitalia.it/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/4.-COIR-2011-XPEED.pdf - F.G. Mangano Early bone formation around immediately loaded implants with nanostructured calcium-incorproated and machined surface: a randomized controlled histologic and histophometric study in human posterior maxilla
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28154996