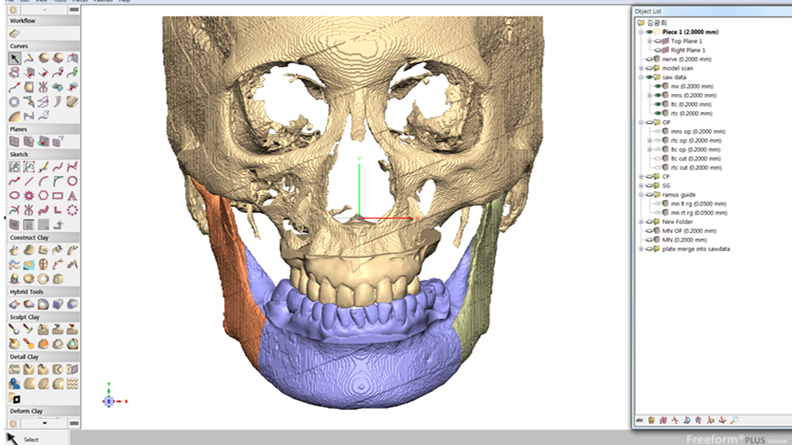
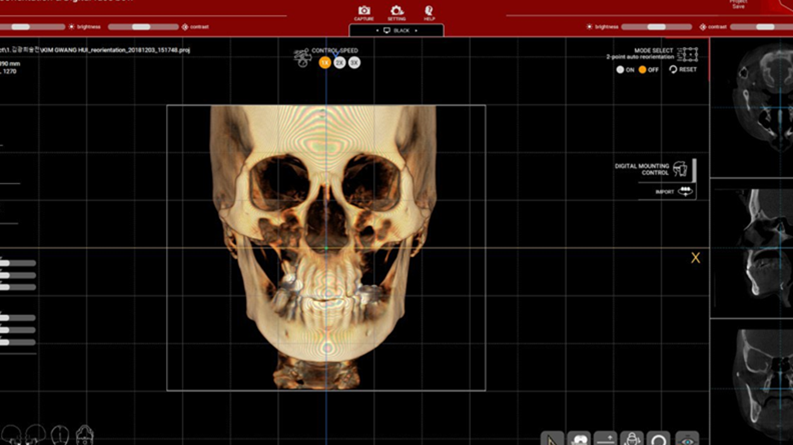
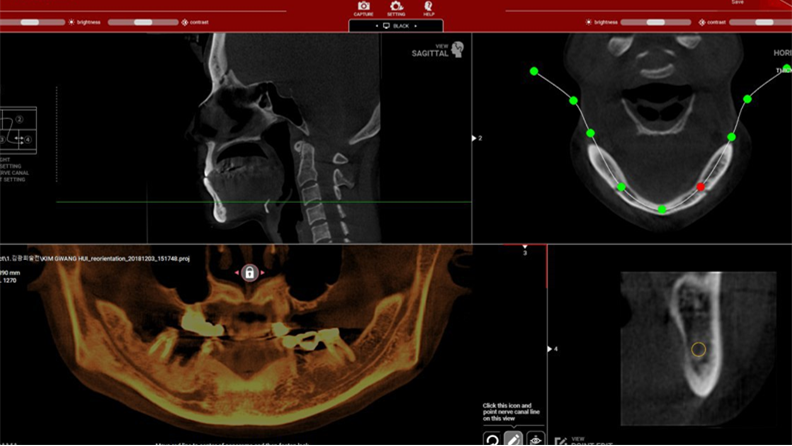
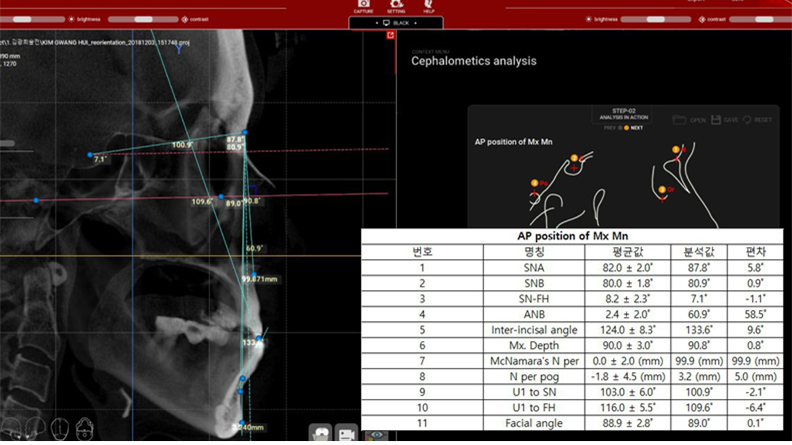
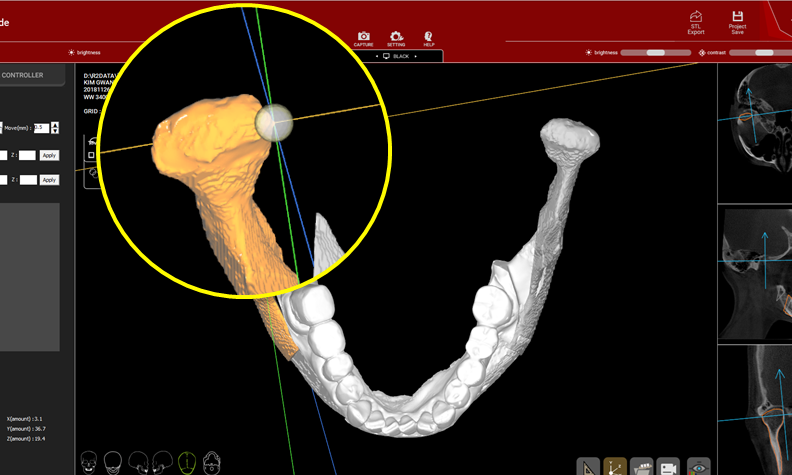
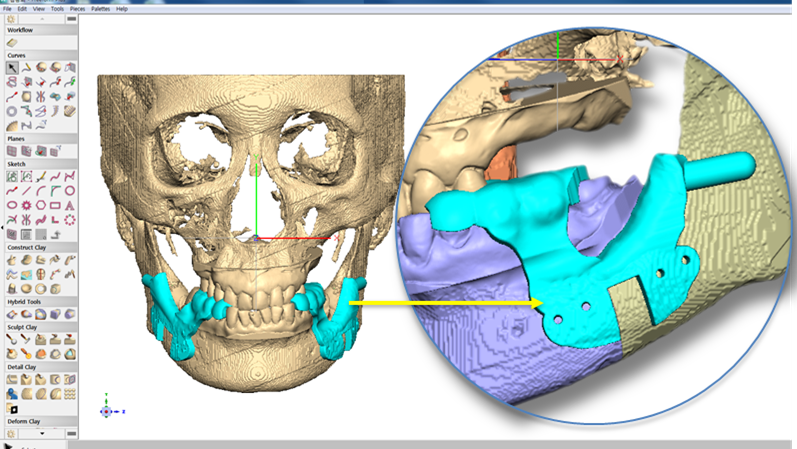
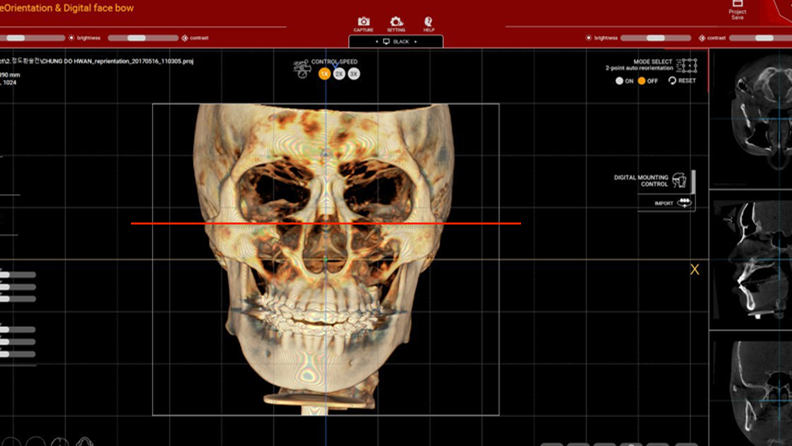
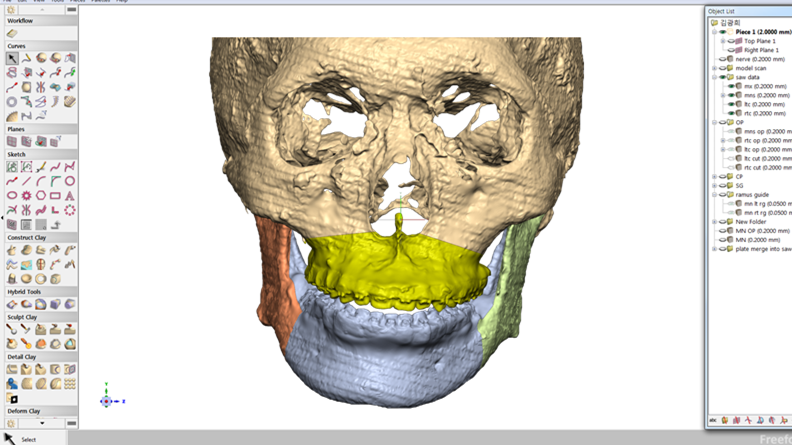
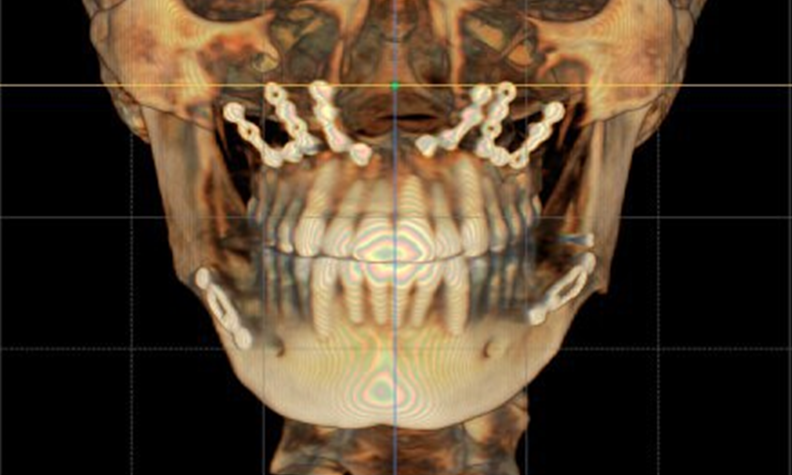
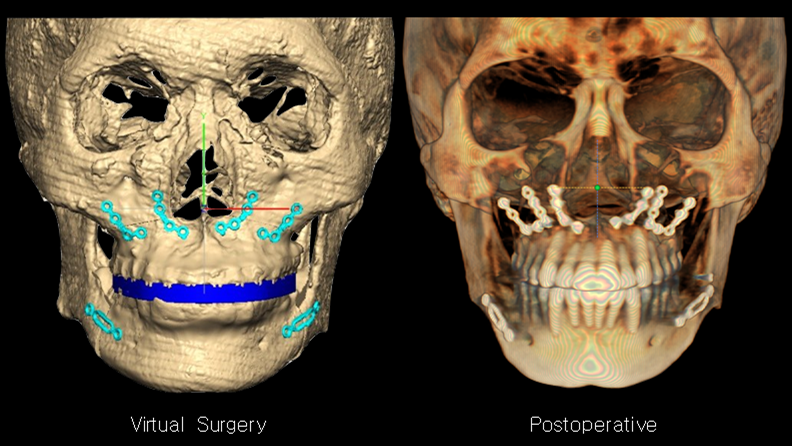
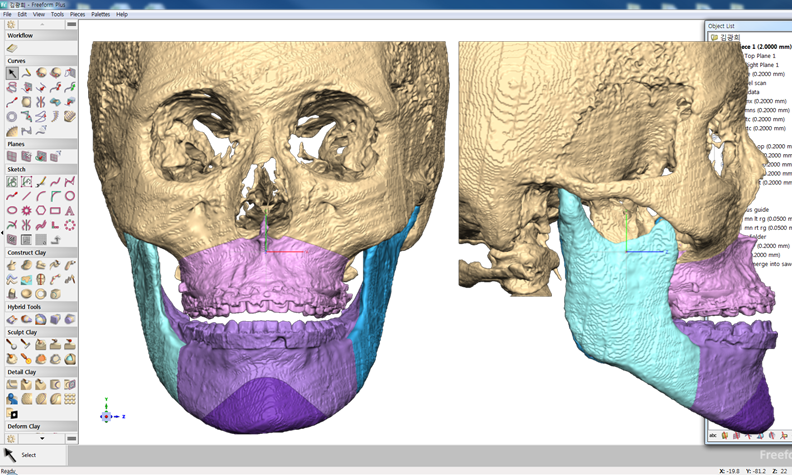
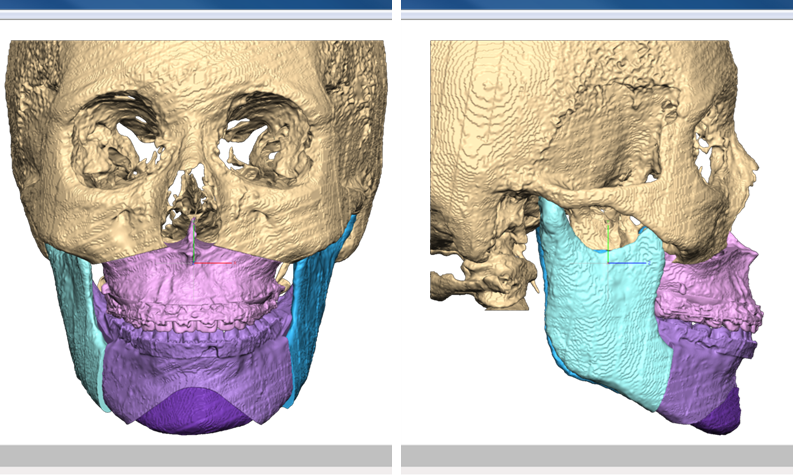
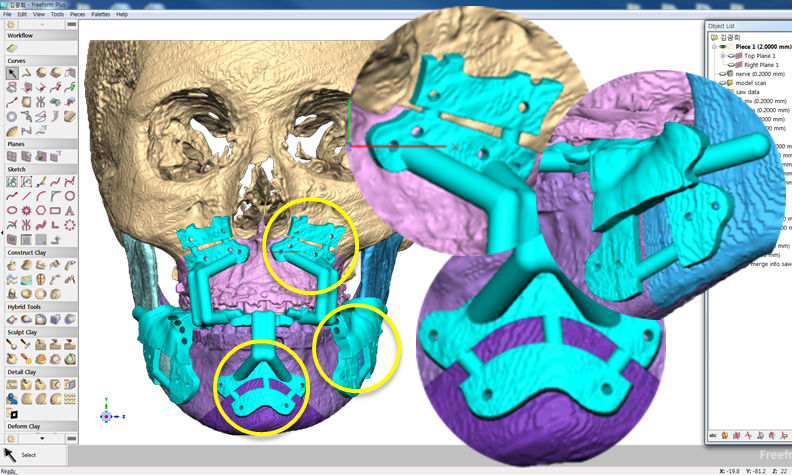
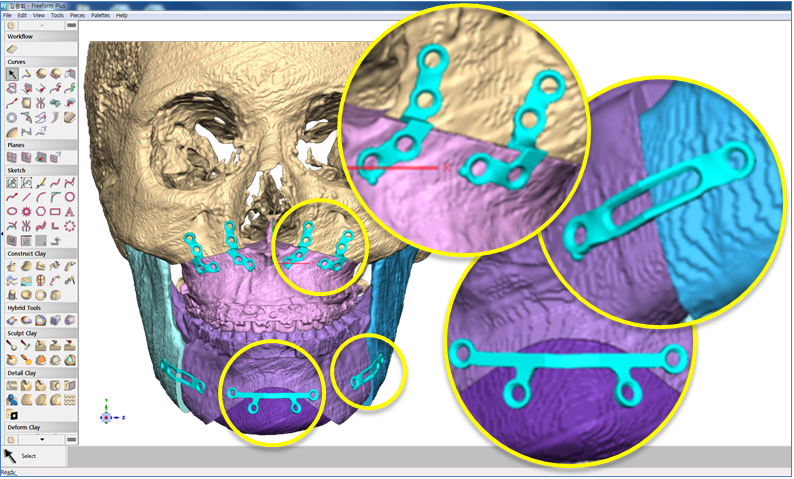
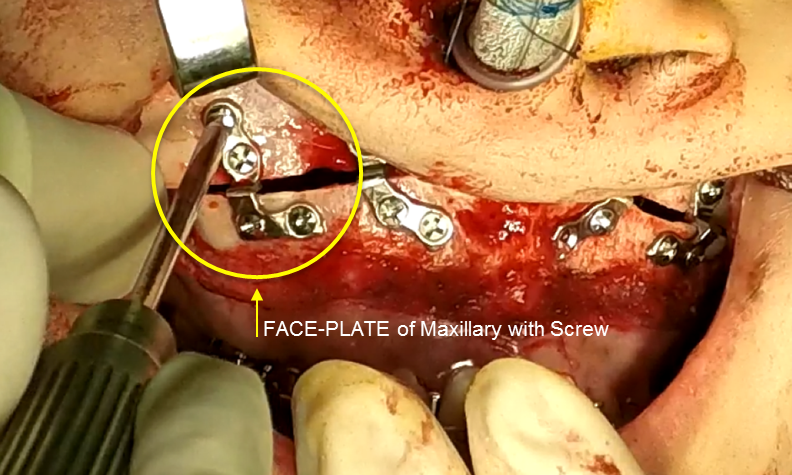
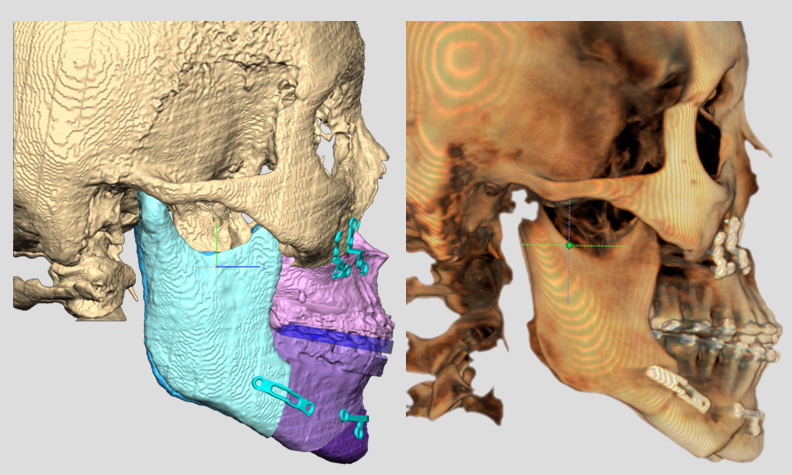
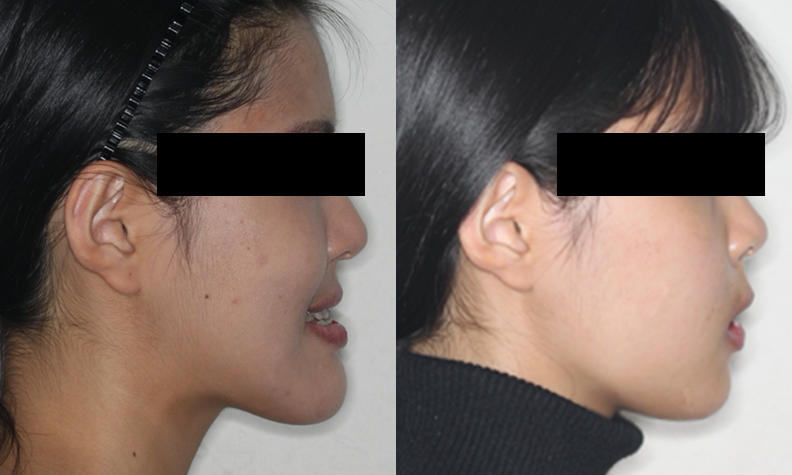
Clinical case: Prognosis Improvement by Implant Placement
- Courtesy of Prof. Byoung-Eun Yang, Korea -
Keywords
Prof. Byoung Eun Yang, BSSRO, 1jaw surgery, virtual surgical simulation, digital orthognathic surgery, FACEGIDE, maxillo-facial surgery, class Ⅲ malocclusion
Products:
R2GATE, FACEGIDE
“ Convenience without bone-fit process, plus more precision ”
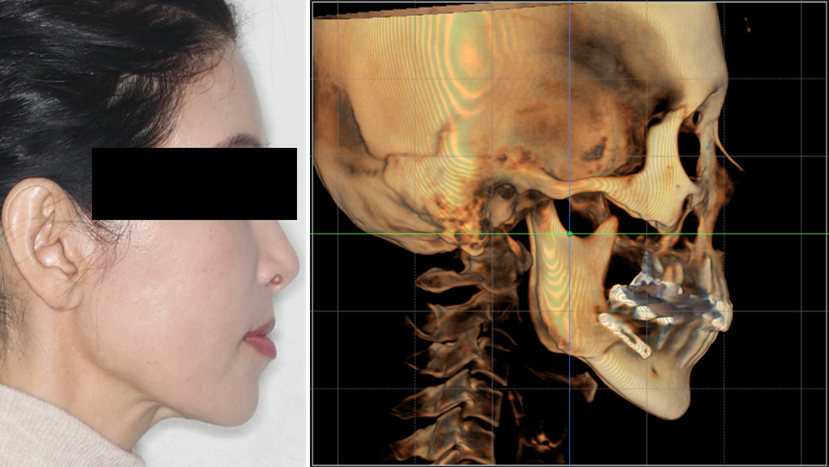
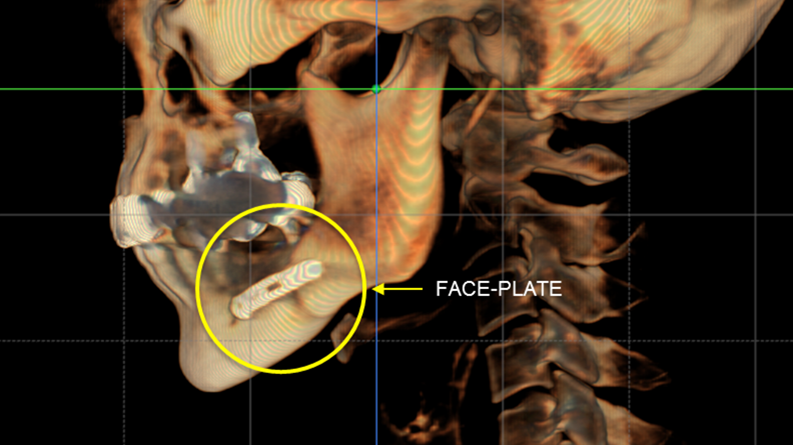
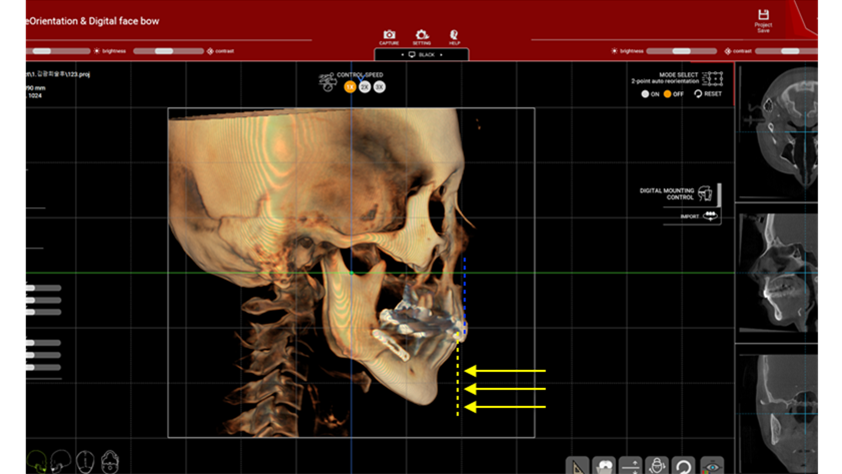
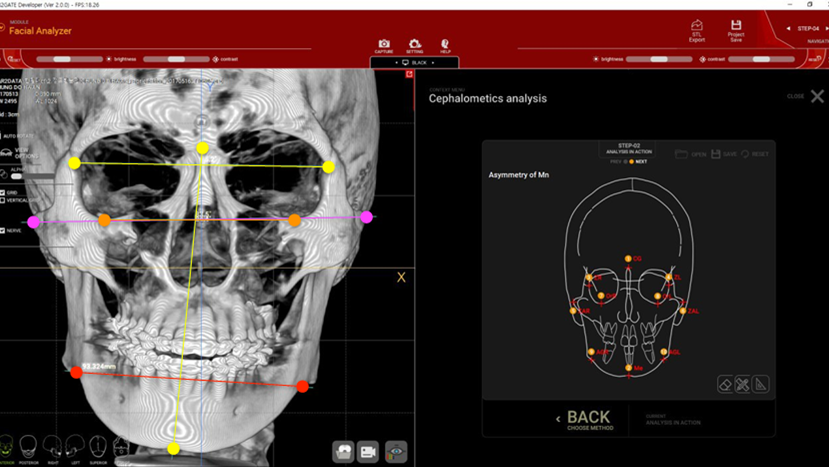
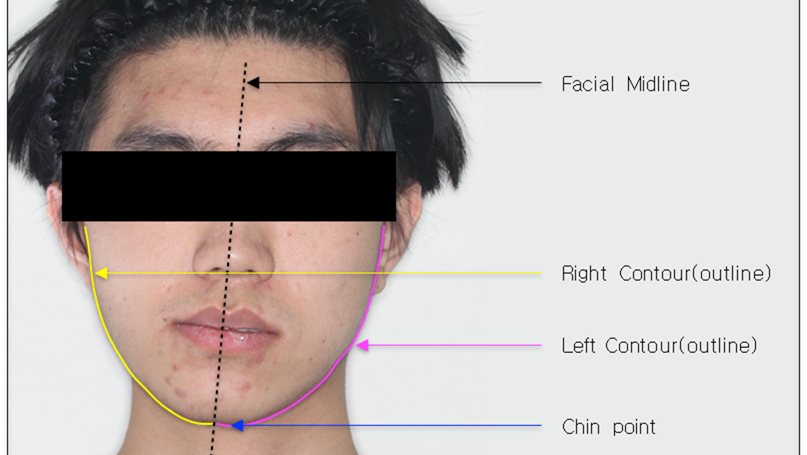
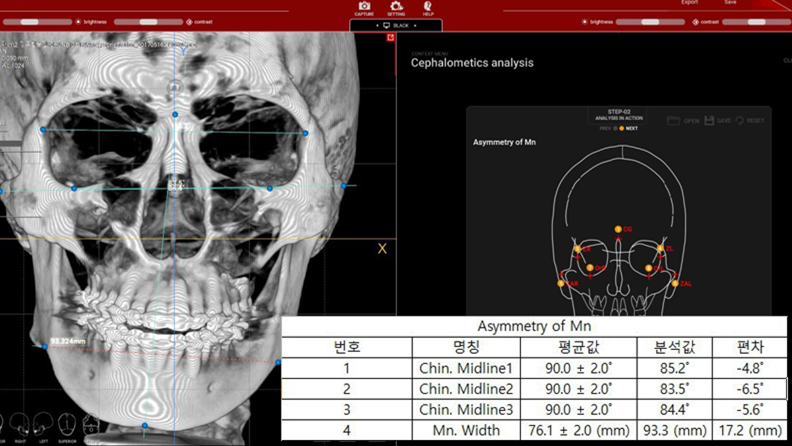
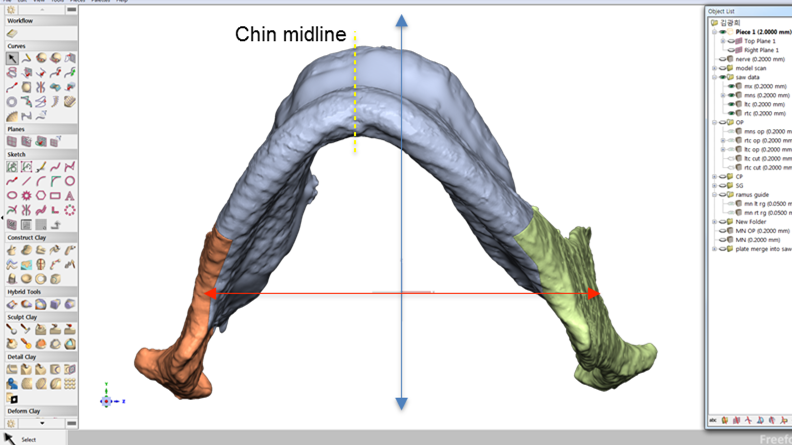
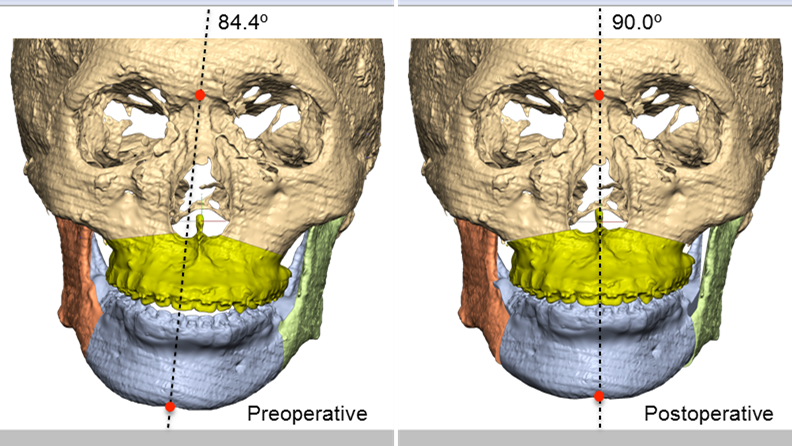
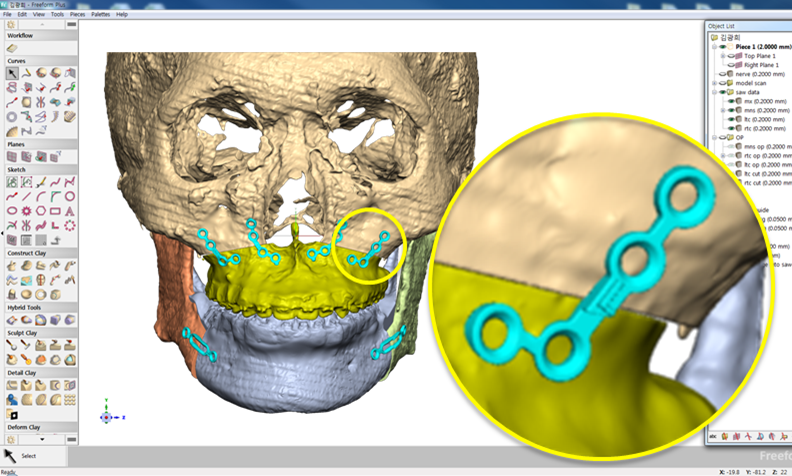
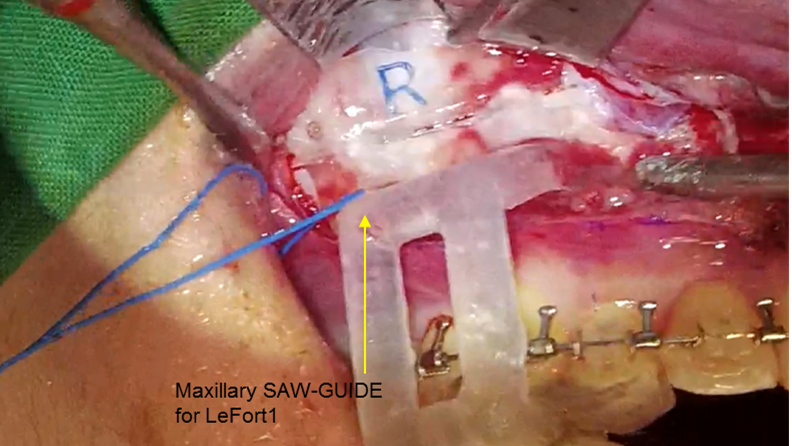
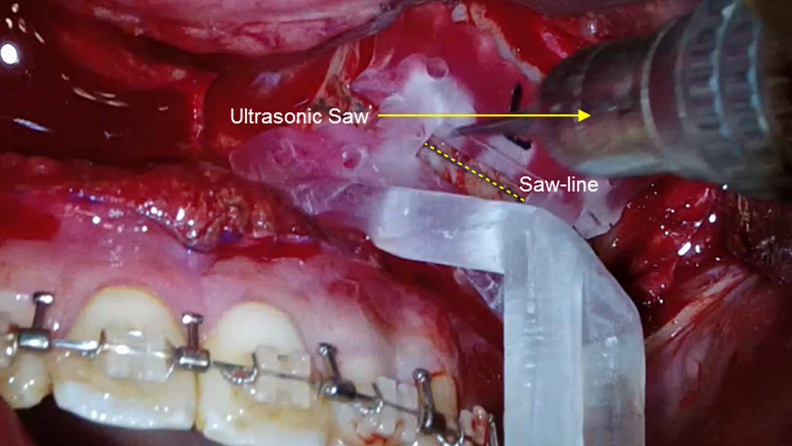
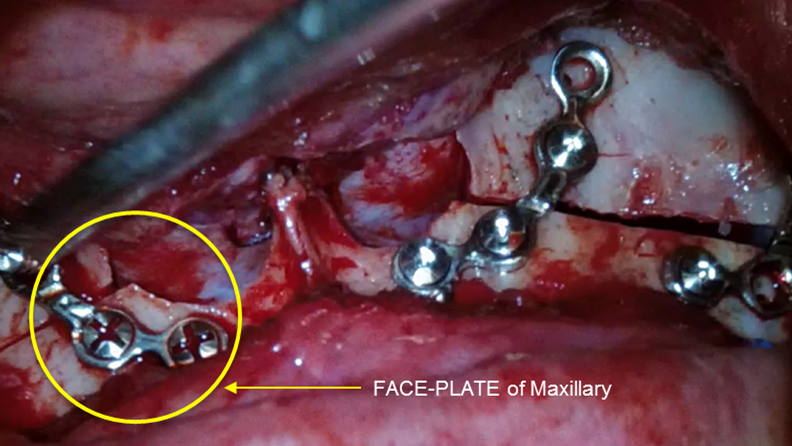
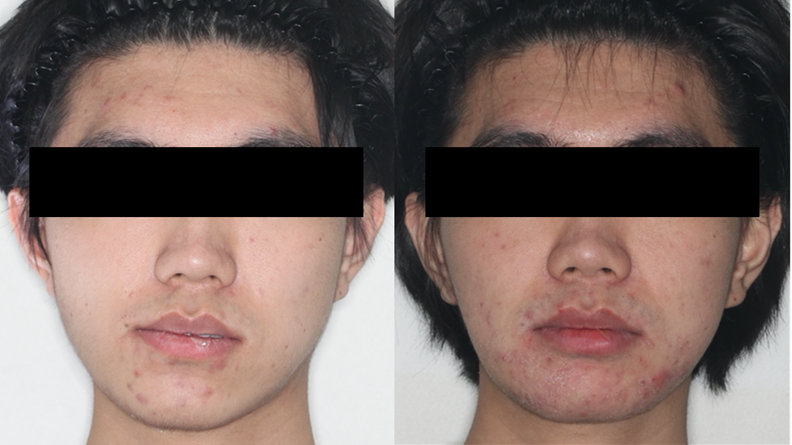
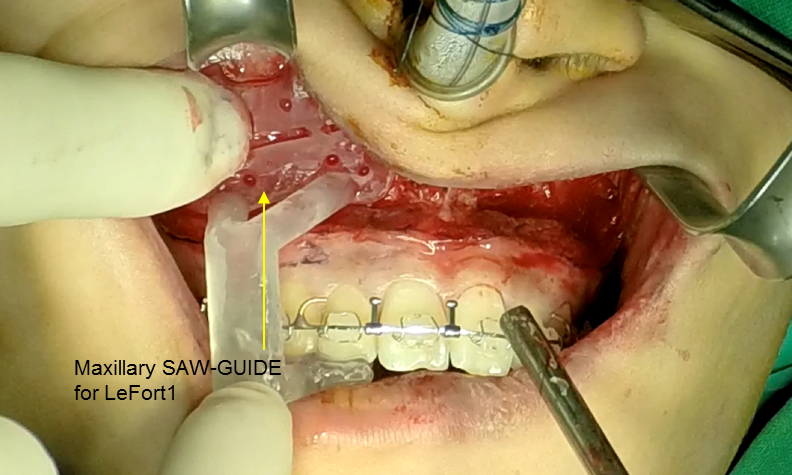
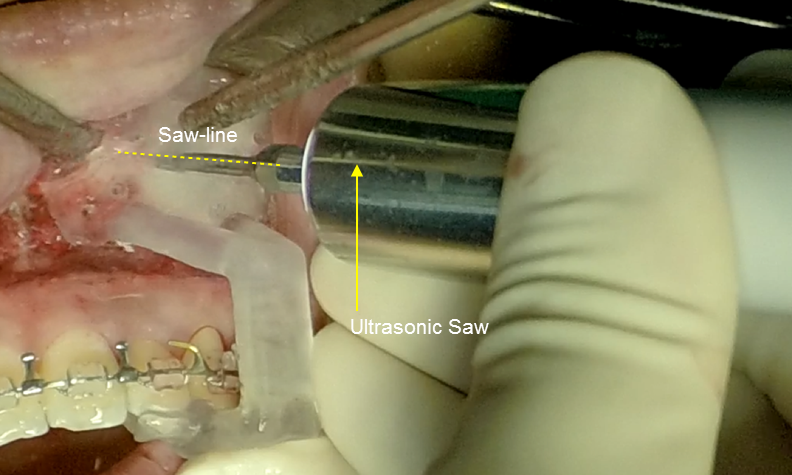
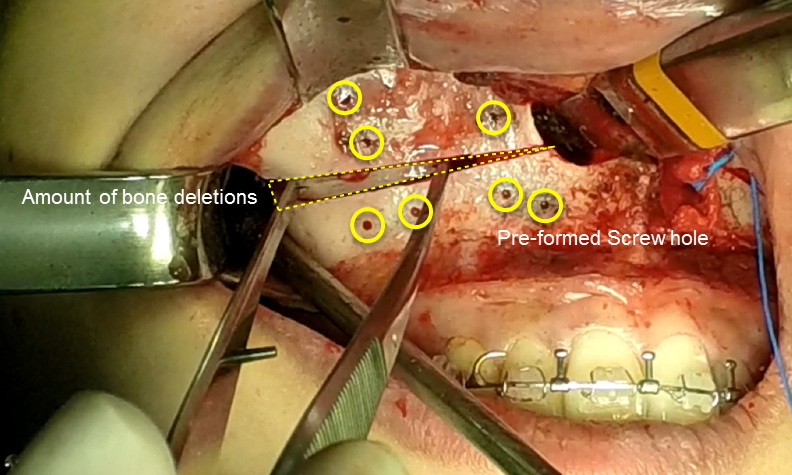
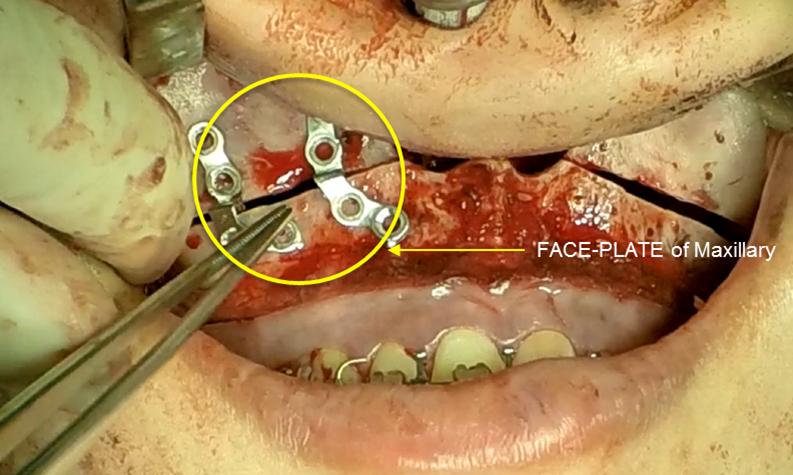
Clinical case: Facial Asymmetry Improvement
- Courtesy of Prof. Byoung Eun Yang, Korea -
Keywords
Prof. Byoung Eun Yang, LeFort1, BSSRO, 2-jaw surgery, virtual surgical simulation, digital orthognathic surgery, FACEGIDE, maxillo-facial surgery, class Ⅲ malocclusion, cross bite, facial asymmetry
Products:
R2GATE, FACEGIDE
“A system that can predict &correct surgical results”
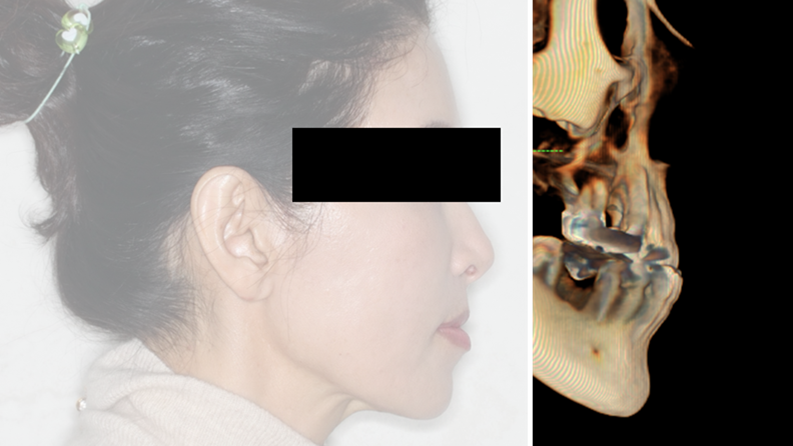
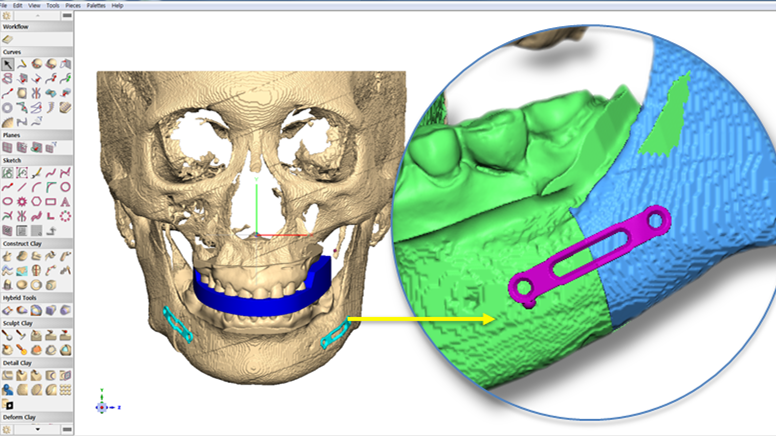
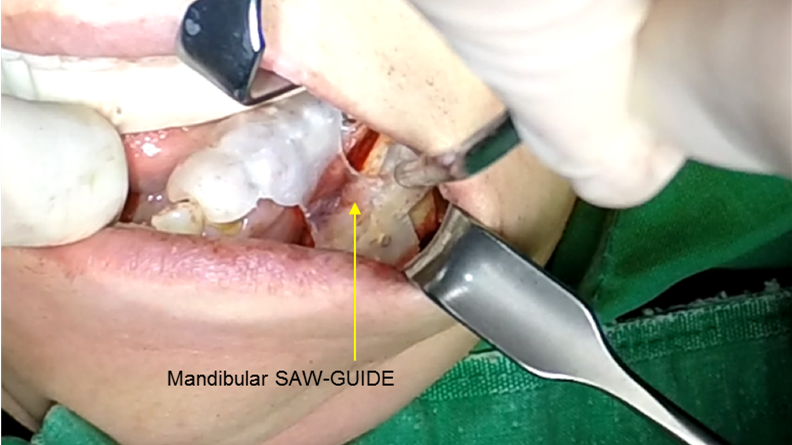
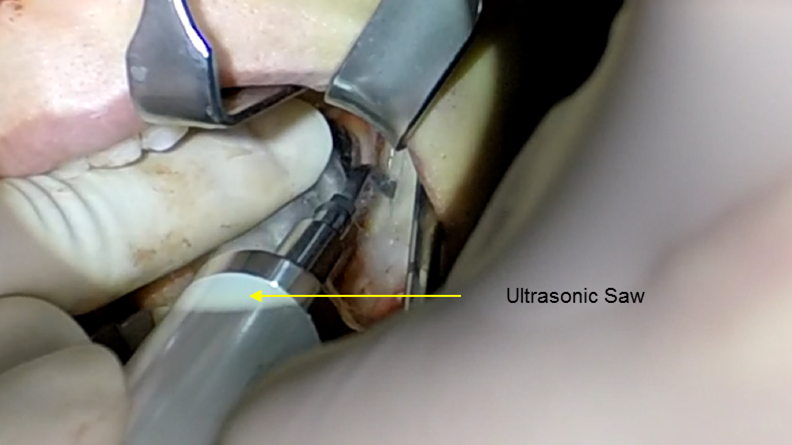
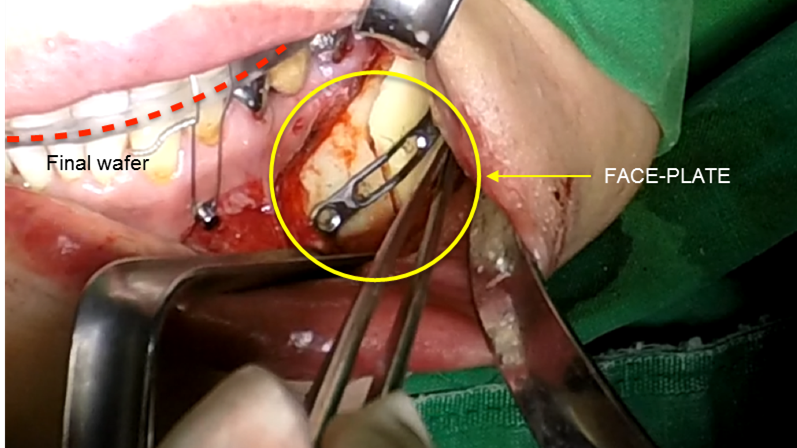
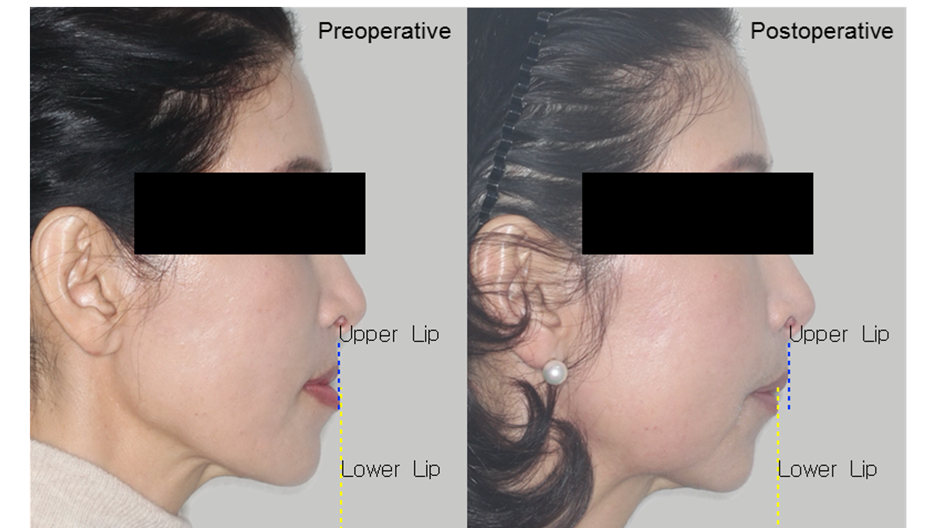
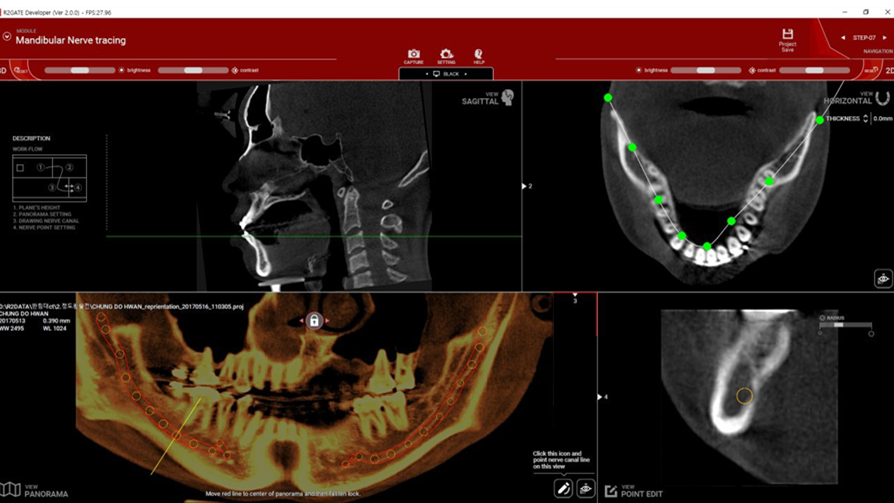
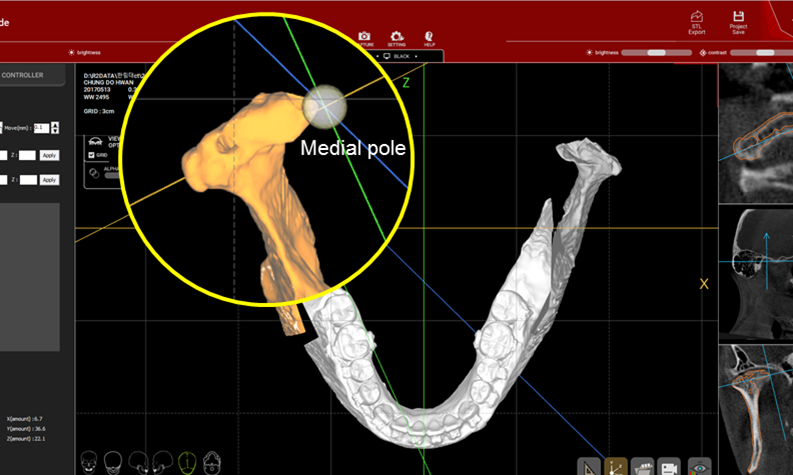
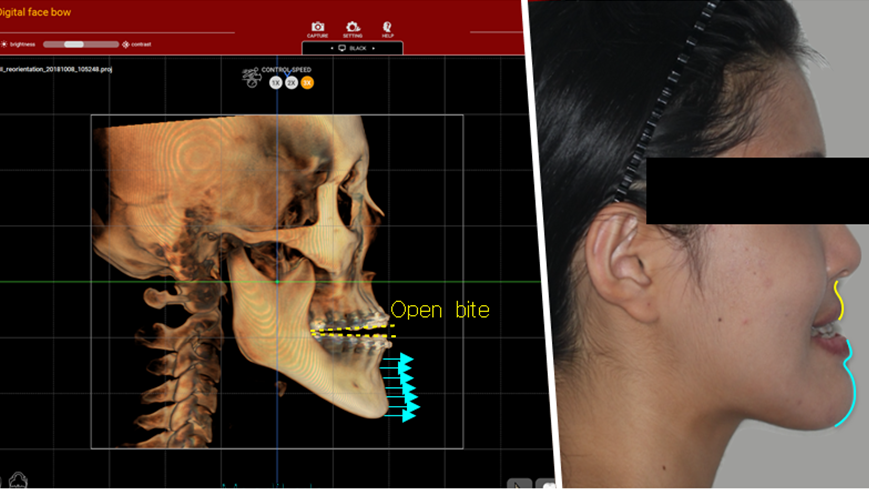
Clinical case: Improved Mandibular Facial
- Courtesy of Prof. Byoung Eun Yang, Korea -
Keywords
Prof. Byoung Eun Yang, LeFort1, BSSRO, 2-jaw surgery, virtual surgical simulation, digital orthognathic surgery, FACEGIDE, maxillo-facial surgery, class Ⅲ malocclusion, cross bite, facial asymmetry
Products:
R2GATE, FACEGIDE

How can primary stability be increased?
Primary stability is especially important in the case of poor quality bone. The instability of dental implants results in fibrous encapsulation and failed osseointegration (Lioubavina-Hack, et al. 2006). One method for increasing primary stability is modifying the surgical technique for implant placement. Studies have reported that the undersized surgical technique, which uses a final drill diameter smaller than the diameter of the implant, results in a higher primary stability when compared with the press-fit technique (Tabassum, et al. 2009, Tabassum, et al. 2010a).
Other studies have reported a higher implant stability with the bone-condensing techniques rather than the bone-drilling technique (Fanuscu, et al. 2007, Markovic, et al. 2011) and conventional techniques rather than the osteotome technique (Cehreli, et al. 2009, Padmanabhan, et al. 2010). The stress distribution of Ti implants with various thread depths has also been investigated using finite element analyses(FEA) to identify the most effective thread depth for stress distribution (Ao, et al. 2010, Chun, et al. 2002, Kong, et al. 2008).
The thread depth also provides a higher contribution than the thread width for stress distribution to the bone (Kong, et al. 2008).
Ti implants with a deeper thread depth provide a higher surface area, which is advantageous for increasing stability in areas of poor quality bone (Abuhussein, et al. 2010). Ti implants with deeper thread depths also facilitate an increased load and mechanical interlocking with poor quality bone.
Another method increasing the primary stability is to change the implant design, such as the shape of the implant body and thread, length, and diameter. Various thread designs for taper implants and other dental implant designs have already been reported to effect the primary stability. Taper implants also show a higher primary stability than cylindrical implants (Kim, et al. 2009, Sakoh, et al. 2006, Wilmes, et al. 2008).
Meanwhile, dental implants with a long length or wide diameter show a significantly increased insertion torque (Kim,et al. 2009, Wilmes, et al. 2008). Plus, dental implants without self-tapping blades have a higher primary stability than implants with self-tapping blades (Kim et al. 2011).
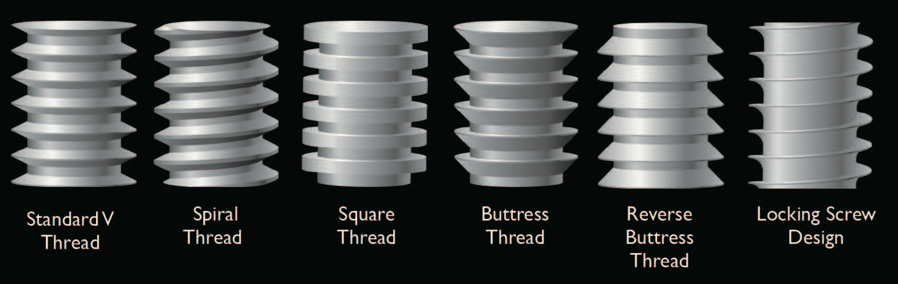
Various fixture thread pattern types
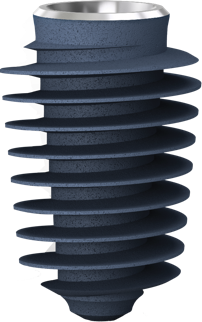
Megagen's KnifeThread®
made totally different ISQ pattern!!
KnifeThread®guarentees
sustauned implant stability
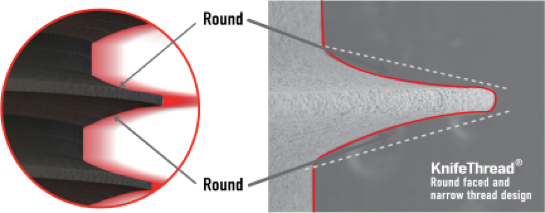
Thanks to MegaGen’s unique KnifeThread® and super self-tapping design, better initial stability can be attained in any compromised bone situation.
The design enables bone condensing, gentle ridge expansion, maximized compressive force resistance, and minimized shear force production.
What is the ideal surface for dental implants?
Since the osseointegration concept was introduced by Branemark in the 1960s, primarily osseointegrated implants have been recommended in the dental treatment area and high implant success rates have been reported. A prerequisite for successful osseointegration is initial stability after implant placement, which depends on the surface characteristics and morphology of the implant and bone density of the surgical site.
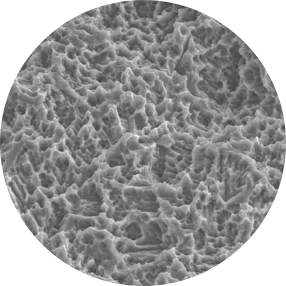
Lately, various surface treatment methods have been studied to facilitate rapid and strong osseointegration. According to the surface roughness and topography, the surface chemistry plays an important role for osseointegration. Titanium (Ti) and Ti alloys are bioinert surfaces and are not able to directly bond with bone. One method for increasing surface reactivity is to coat the Ti surface with nanostructured calcium. Many in vitro and in vivo studies have already reported the effectiveness of nanostructured calcium coating.
For example, in vitro studies have reported that surface modification using calcium ions increased the growth of osteoblastic cells and promoted the precipitation of apatite on Ti surfaces in simulated body fluid. Plus, the effects of cell adhesion to calcium-incorporated Ti surfaces were reduced in human alveolar bone cells and MG-63 cells, and increased in human osteoblasts. Several in vivo studies have reported that incorporating calcium into Ti implants by hydrothermal treatment stimulated osseointegration by increasing the BIC % when compared with untreated Ti implants in rabbit models.
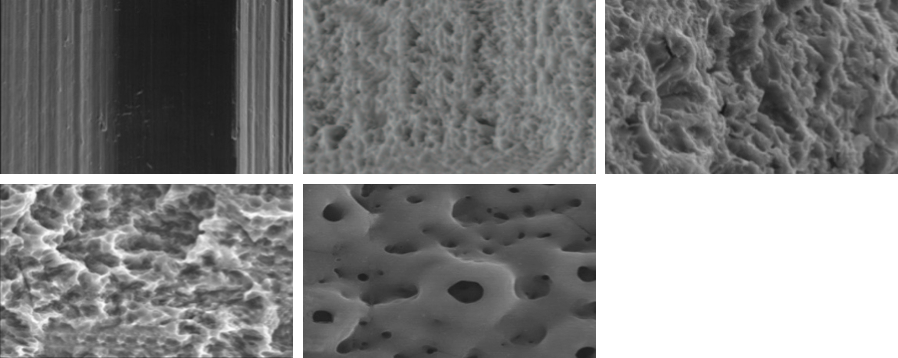
Various surface treatments
Surface treatment technology
guarantees an excellent result.

1. Nano bone matrix layer of Ca2+ -incorporated S-L-A surface
2. Fast & strong osseointegration
3. Dual check system for greater safety
Ca2+ is incorporated into the fixture structure to create a CaTiO3 nano-structure. This then forms a unique & uniform nano-structure with Ca2+ions, which activate osteoblasts in living organisms.